Observing Occultations Primer
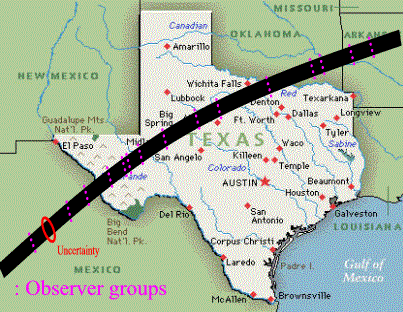
Groups of observers place themselves along the path in a
perpendicular slice of that path (see the dots on the map above):
 |
Predictions: The IOTA software creates
predictions based on the current orbital data.
|
 |
Path notes:
 |
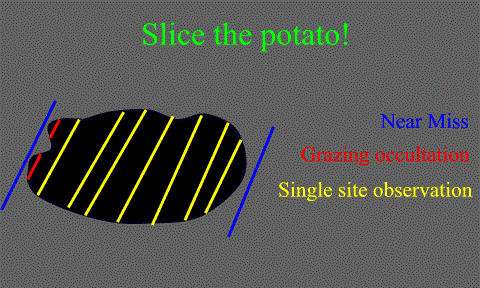
Imagine a lumpy potato casting a shadow.
|
 |
Move that potato and the shadow follows those
movements.
|
 |
For the duration of the event, the potato is frozen
in place.
|
 |
Putting observers in brackets perpendicular to the
path (groups of red dots above) will "slice the
potato" and define small part of the asteroid's
profile. Combining the data (stacking the
slices) gives us a rough shape of the asteroid.
|
 |
The more slices, the more detail we can gain.
|
 |
Near misses define the outer limits of the asteroid
size.
|
 |
Grazing occultations define profiles in high detail.
|
 |
Full slices define a small section
|
 |
The time it occults the star fixes the asteroid in
the sky. Taken with other observations, that
helps refine the asteroid's orbit.
|
|
Placement
 |
Ideally, groups would assign people along the center, out to
the edge of the shadow, and just outside the predicted path
to give full coverage.
|
 |
Each person within a group would observe a slightly
different profile of the blocking body. For a
50km-wide path, observers spaced 7-10km apart would give
useful profiles.
|
How do we time occultations?
Before the Event:
 |
Look up the finder charts and familiarize yourself with the
star and the surroundings. (See the "equipment
required" {below} for location of the predictions.)
|
 |
If possible, view the star a few nights before the event.
|
 |
Test your equipment well before the event.
|
 |
Gather everything you'll need in a kit so you're sure you
bring everything along.
|
 |
Practice with the reaction testing software - http://lunar-occultations.com/iota/aops.htm
|
 |
Practice observing and finding the star.
|
Visual Observations
The easiest method, but accuracy is dependant upon the observer's
abilities.
 |
Equipment Required:
 |
Telescope - Motorized helps, but any scope that can
see the target star will do.
|
 |
Timing Device
 |
Normally a radio tuned to WWV (short wave)
|
 |
If coordinated, a local FM radio can
substitute
|
|
 |
Voice Recorder with microphone. Usually a
standard cassette or mini voice recorder.
|
 |
Occultation info (finder charts, timing info) with
recent updates from:
|
|
 |
Process:
 |
Tune the radio to WWV and set the volume so the tape
recorder can record it and your voice.
|
 |
Use the finder chart and set the scope to center on
the star.
|
 |
When the star winks out, call "out".
When the star reappears, call "in".
 |
A clicker of some sort would help increase
the accuracy of the timing by producing a
quicker sound.
|
|
 |
Ensure the timing ticks from WWV are recorded both
before and after the event.
|
|
What does it tell us?
 |
At the most basic, the star helps outline the blocking
object. This will define:
 |
The orbit, size, and shape of the blocking object
|
 |
The mountain and valley profile of the moon (during
a grazing occultation)
|
 |
Small moonlets of asteroids
|
 |
Close companion stars that can't be split any other
way
|
 |
Redefine the star's position
|
|
 |
If the dark object is airless, the occultation appears like
switching off a light.
|
 |
If the dark object has an atmosphere, the occultation is
likely to dim or change, then wink out, then reappear dim
and then come back to the original magnitude.
Sometimes, scientists can read the change in the light
spectrum and determine the gasses in the atmosphere.
Most of the time, this can help define the depth of the
atmosphere.
|
 |
Asteroids & airless moons - it will suddenly blink off
and back on
|
 |
Very close, very large stars can sometimes produce a stepped
event where the star gradually disappears rather than
winking on or off.
|
 |
Planets and moons with an atmosphere will also dim
gradually.
|
 |
|
Why volunteer?
 |
Occultations happen randomly throughout the surface of the
Earth. Some will happen in your neighborhood and your
backyard.
|
 |
Professional astronomers are collected at large
observatories (Hawaii, Chile, the Rockies, & sites in
Europe & Japan) or at universities. They or their
equipment are likely to be too busy to observe
occultations. Their equipment may not be suitable for
occultation observations.
|
 |
Amateur astronomers are scattered around the world and have
equipment suitable to occultation observation.
|
 |
Amateurs are also willing to donate time and effort to the
project.
|
 |
The observations return valuable information to expand our
scientific knowledge.
|
 |
This knowledge may help scientists defend the Earth from
encroaching asteriods!
|
|
|
|